Lithium industry
Decowell remote I/O module is used in lithium battery chemistry equipment
Lithium battery capacity separation equipment

The production process of lithium batteries is divided into three stages: front, middle, and back: the backstage is detection and packaging, and
the core process is formation and capacity separation.
The backstage is the electrochemical link, which mainly includes battery cell formation, capacity separation, packaging, and final inspection of
battery packs. Formation and capacity separation are the main processes, with a high value. One piece of equipment requires about 4 million
USD and a single line requires 30,000 to 40,000 channels.
Among them, the charging and discharging machine is the key equipment in capacity separation, and it is also the most used equipment in
the backstage.
01 Industry process
The transferred lithium-ion battery needs to go through three processes liquid injection, formation, and aging to prepare the finished battery.
Afterwards, it will be subjected to capacity separation, OCV, K value, thickness and other tests, sorting and grading, and then packaging and
shipment.
Formation is the process of charging the battery with a small current after liquid injection, including pre-formation and formation.
Capacity classification is the process of performing certain charge and discharge tests on batteries and classifying them by capacity. Post-process
classification is the process of separating batteries according to product grade standards by testing various battery performance and product
indicators (capacity, voltage, internal resistance, K value, thickness, appearance, etc.).
02 Module application
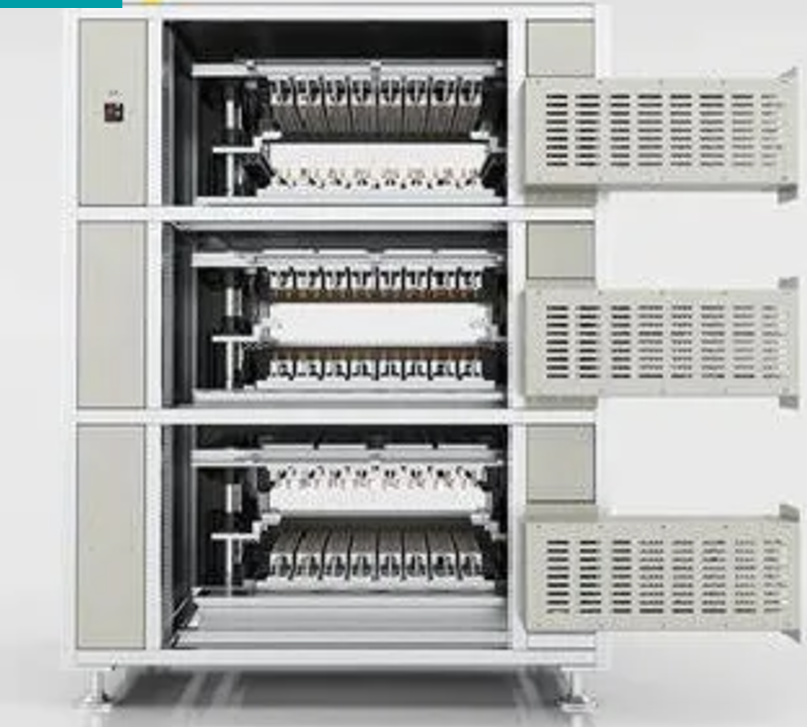
A single cabinet is a composite installation, using 48 card-type remote I/Os on both sides AB. A large number of digital signals are used for
battery loading and unloading control and signal indicators at various positions of the cabinet. Analog inputs are safety signals such as
temperature detection and smoke detection. This environment requires remote I/O to have a high level of electromagnetic protection. This
solution is in line with the layout of distributed solutions and perfectly replaces the Siemens 1200 local I/O solution.

Application highlights:
There are many types of I/O modules, a wide range of application scenarios, and solutions for various types of products.
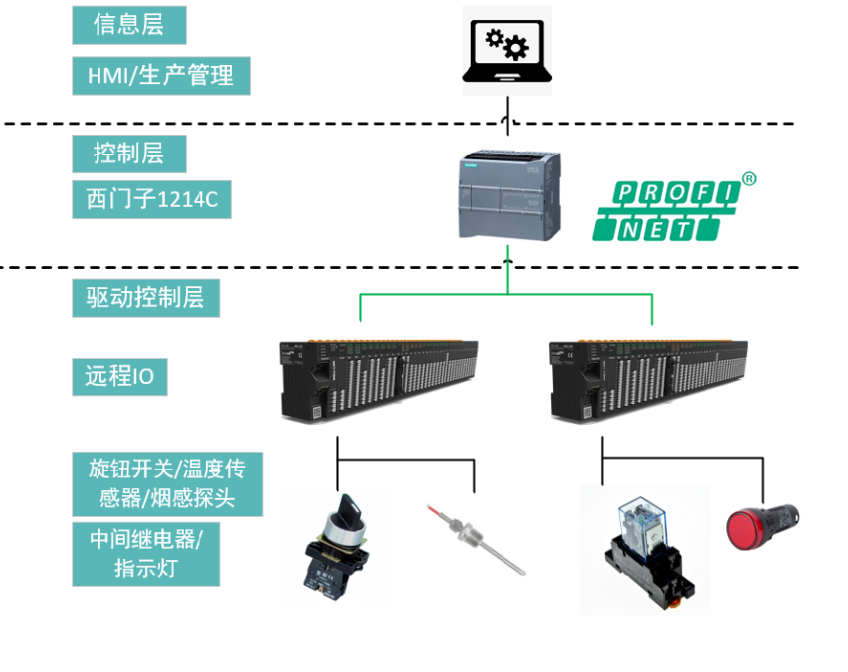
03 Device topology diagram
04 Decowell EX series remote I/O
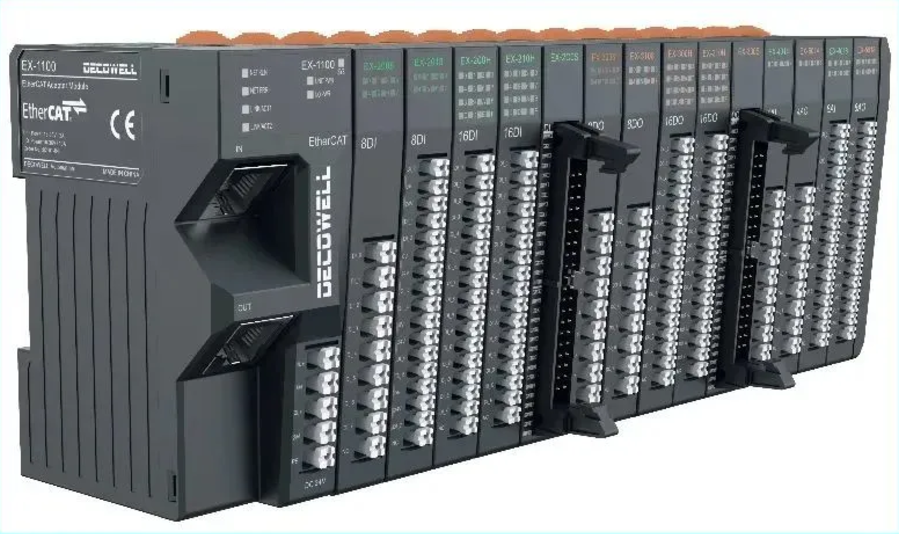

Product features:
1. Stable communication, fast response, convenient operation, and high efficiency;
2. Rich bus protocols, supporting multiple communication protocols, such as EtherCAT, PROFINET, DeviceNet, CC-Link, Ethernet/IP,
Modbus-RTU, CC-Link IEF Basic, etc.;
3. Rich signal types, which can meet factory automation and process automation control. Support digital quantity, analog quantity,
temperature module, encoder module, free communication module;
4. Compact structure, small module size, a single I/O module supports up to 32 digital signal points;
5. Strong expansion capability, a single adapter can expand up to 32 I/O modules, and the coupler scans quickly;
6. Simple and easy to use, standard DIN35 rail installation, plug-in terminals, and tool-free installation.